For each of the following compounds, indicate whether or not it can exist as cis–trans stereoisomers. If it can exist as the two isomers, draw both as a condensed structure.
(a) H2C=CHCH2CH3

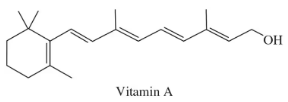
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


For each of the following compounds, indicate whether or not it can exist as cis–trans stereoisomers. If it can exist as the two isomers, draw both as a condensed structure.
(a) H2C=CHCH2CH3
For each of the following compounds, indicate whether or not it can exist as cis–trans stereoisomers. If it can exist as the two isomers, draw both as a condensed structure.
(d)
For each of the following compounds, indicate whether or not it can exist as cis–trans stereoisomers. If it can exist as the two isomers, draw both as a condensed structure.
(c)
The vision process in animals involves the change of one double bond in retinal from its cis form to its trans form. The structures of cis and trans retinal are shown below. Label which is cis and which is trans.
Determine whether each of the following is the cis or the trans stereoisomer:
(c)
Determine whether each of the following is the cis or the trans stereoisomer:
(b)