What effect do the listed changes have on the position of the equilibrium in the reaction of carbon with hydrogen?
C(s) + 2 H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) ∆H = -18 kcal/mol (-75kJ/mol)
b. Increasing pressure by decreasing volume

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

What effect do the listed changes have on the position of the equilibrium in the reaction of carbon with hydrogen?
C(s) + 2 H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) ∆H = -18 kcal/mol (-75kJ/mol)
b. Increasing pressure by decreasing volume
What effect do the listed changes have on the position of the equilibrium in the reaction of carbon with hydrogen?
C(s) + 2 H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) ∆H = -18 kcal/mol (-75kJ/mol)
c. Allowing CH4 to escape continuously from the reaction vessel
Two curves are shown in the following energy diagram:
b. Which curve represents the spontaneous reaction, and which the nonspontaneous?
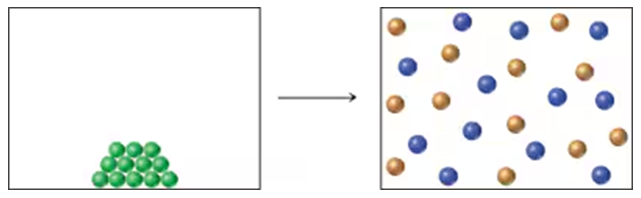
The following diagram portrays a reaction of the type A(s) → B(g) + C(g), where the different-colored spheres represent different molecular structures. Assume that the reaction has ∆H = +9.1 kcal/mol (+38.1 kJ/mol).
b. Is the reaction likely to be spontaneous at all temperatures, nonspontaneous at all temperatures, or spontaneous at some but nonspontaneous at others?
Is the total enthalpy (H) of the reactants for an endothermic reaction greater than or less than the total enthalpy of the products?
The vaporization of Br2 from the liquid to the gas state requires 7.4 kcal/mol (31.0 kJ/mol).
a. What is the sign of ∆H for this process? Write a reaction showing heat as a product or reactant.