Compare the ∆Hvap values for water, isopropyl alcohol, ether, and ammonia, and order them from lowest to highest. Explain the rank order based on intermolecular attractive forces.

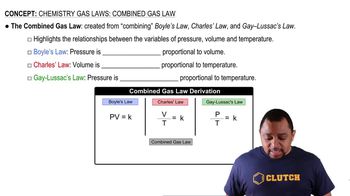
Which assumptions of the kinetic–molecular theory explain the behavior of gases described by Boyle's law? Explain your answer.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Kinetic-Molecular Theory

Boyle's Law
Assumptions of Gas Behavior

Assume that you have a sample of gas at 350 K in a sealed container, as represented in part (a). Which of the drawings (b)–(d) represents the gas after the temperature is lowered from 350 K to 150 K and if the gas has a boiling point of 200 K? Which drawing represents the gas at 150 K if the gas has a boiling point of 100 K?
<IMAGE>
List four common units for measuring pressure.
Which assumptions of the kinetic–molecular theory explain the behavior of gases described by Charles's law? Explain your answer.
Which assumptions of the kinetic–molecular theory explain the behavior of gases described by Gay-Lussac's law? Explain your answer.
A gas has a volume of 2.84 L at 1.00 atm and 0 °C. At what temperature does it have a volume of 7.50 L at 520 mmHg?
