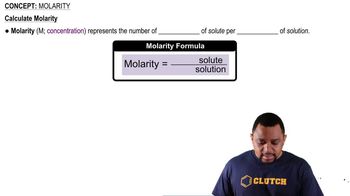
The solubility of CO2 gas in water is 0.15 g/100 mL at a CO2 pressure of 760 mmHg.
b. An atmospheric concentration of 380 ppm, CO2 corresponds to a partial pressure of 0.00038 atm. What percentage of the CO2 originally dissolved in the solution in part (a) remains in solution after the soft drink reaches equilibrium with the ambient atmosphere?