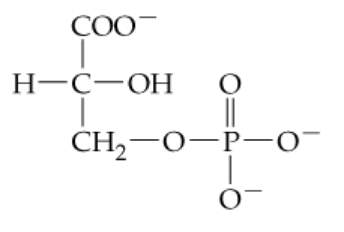
Identify the functional group in the following compounds and give the structures of the products of hydrolysis for these compounds.
a.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Identify the functional group in the following compounds and give the structures of the products of hydrolysis for these compounds.
a.
Identify the functional group in the following compounds and give the structures of the products of hydrolysis for these compounds.
b. CH3CH2OPO32-
N-Acetylglucosamine (also known as NAG) is an important component on the surfaces of cells.
b. Draw the structures of the products of acid hydrolysis.
Consider the following unnatural amino acid:
a. If two molecules react to form an ester, what is the structure of the ester product?
Consider the following unnatural amino acid:
c. Draw the cyclic ester resulting from the intramolecular reaction of the hydroxyl group of this amino acid with its carboxyl group (cyclic esters are called lactones).
Draw the structures of the following compounds and use dashed lines to indicate where they form hydrogen bonds to other molecules of the same kind: (ii) methyl formate