How many ways can four different amino acids be arranged in a peptide so that each peptide is unique?

Complete the following two sentences with either globular or fibrous:
a. Proteins with secondary structure composed primarily of alpha-helix are___________ proteins.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Globular Proteins

Fibrous Proteins

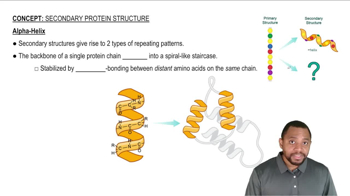
Alpha-Helix Structure
Examine the α-helix in Figure 18.1 and determine how many backbone C and N atoms are included in the loop between an amide hydrogen atom and the carbonyl oxygen to which it is hydrogen bonded.
Consult the β-sheet in Figure 18.2 and (a) name the bonding responsible for the sheet formation and (b) identify the specific atoms responsible for this bonding.
For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
a. Cholesterol is attached to this protein in order to move through the blood system.
For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
b. Ionized zinc is attached to this protein so the protein can function.
For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
c. Phosphate groups are attached to this protein.
