Draw the structure that completes the mutarotation reaction between the two cyclic forms of (a) galactose and (b) fructose.
a.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Draw the structure that completes the mutarotation reaction between the two cyclic forms of (a) galactose and (b) fructose.
a.
Draw the structure that completes the mutarotation reaction between the two cyclic forms of (a) galactose and (b) fructose.
b.
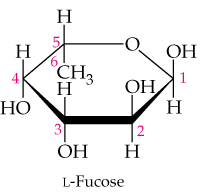
In the monosaccharide hemiacetal shown below number all the carbon atoms, identify the anomeric carbon atom, and identify it as the α or β anomer.
Draw the structure of the α and β anomers that result from the reaction of methanol and ribose. Are these compounds acetals or hemiacetals?
How would you classify the link between the monosaccharides in cellobiose?
During the digestion of starch from potatoes, the enzyme α-amylase catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch into maltose. Subsequently, the enzyme maltase catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose into two glucose units. Write an equation (in words) for the enzymatic conversion of starch to glucose. Classify each of the carbohydrates in the equation as a disaccharide, monosaccharide, or polysaccharide.