Textbook Question
The pathway that converts glucose to acetyl-CoA is often referred to as an “aerobic oxidation pathway.”
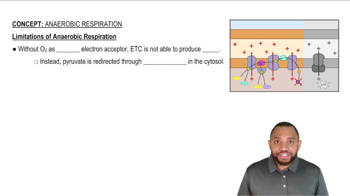
(b) Thinking back to Chapter 20, where does molecular oxygen enter the picture?
885
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
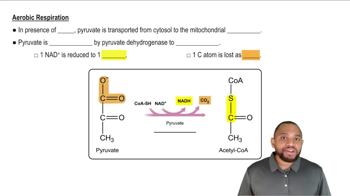

The pathway that converts glucose to acetyl-CoA is often referred to as an “aerobic oxidation pathway.”
(b) Thinking back to Chapter 20, where does molecular oxygen enter the picture?
What are the major monosaccharide products produced by digestion of carbohydrates?
What are the products of digestion of proteins, triacylglycerols, maltose, sucrose, lactose, and starch?
What is the major purpose of the pentose phosphate pathway? What cofactor (coenzyme) is used?
Which cells, liver, muscle, or brain, use the following pathways?
a. Glycolysis
Which cells, liver, muscle, or brain, use the following pathways?
b. Gluconeogenesis