Textbook Question
How are the two strands of nucleic acid in DNA held together?
664
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

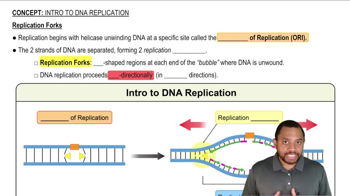

How are the two strands of nucleic acid in DNA held together?
Write the base sequence in a complementary DNA segment if each original segment has the following base sequence:
d. C T G T A T A C G T T A
Write the base sequence in a complementary DNA segment if each original segment has the following base sequence:
d. A T A T G C G C T A A A
What process ensures that the replication of DNA produces identical copies?
How many daughter strands are formed during the replication of DNA?
What are the three different types of RNA?