Textbook Question
Bacteria that convert nitrogen gas into ammonia are __________ .
a. nitrifying bacteria
b. nitrogenous
c. nitrogen fixers
d. nitrification bacteria
650
views
 Bauman 6th Edition
Bauman 6th Edition Ch. 14 - Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology
Ch. 14 - Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology Problem 14.1a
Problem 14.1a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Bacteria that convert nitrogen gas into ammonia are __________ .
a. nitrifying bacteria
b. nitrogenous
c. nitrogen fixers
d. nitrification bacteria
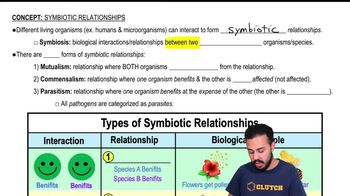
In which type of symbiosis do both members benefit from their interaction?
a. mutualism
b. parasitism
c. commensalism
d. pathogenesis
Endotoxin, also known as ___________, is part of the outer (wall) membrane of Gram-negative bacteria.
Infections that may go unnoticed because of the absence of symptoms are called __________ infections.
List three conditions that create opportunities for pathogens to become harmful in a human.
List three portals through which pathogens enter the body.