- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

A 42.0 N block is resting on a horizontal floor. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the block and the floor are 0.46 and 0.29 respectively. A child is leaning against the block applying a horizontal force. Determine the least horizontal force the child must apply to move the crate at constant velocity.
A 29 kg luggage is resting on the floor in your house. You pull the luggage with an increasing horizontal force. The box moves when your pull is greater than 211 N. The luggage moves with a constant velocity of 1.8 m/s when you reduce the pull to 147 N. How hard must you pull to accelerate the box at 1.5 m/s2?
A 25 kg block is resting on a level truck. You pull the box with an increasing horizontal force. The box moves when the pull is greater than 186 N. You realize that the box moves with a constant velocity of 1.4 m/s when you decrease the pull to 114 N. Determine the static and kinetic friction coefficients between the box and the truck.
Kinetic and static friction are determined experimentally by applying a horizontal force on an object until it moves and for some time after it starts moving. In one such experiment, a 86 N box is placed on a rough horizontal bench and pushed by a horizontal force. The graph below shows the friction force on the box as a function of the push. In what regions of the graph does static and kinetic friction occur?

A goods truck is carrying a 25 kg box. Draw a free-body diagram showing all the forces on the box if the truck is speeding up in the eastward direction. Consider the coefficient of static friction = 0.45 and the coefficient of kinetic friction = 0.25.
A rugby player kicks a 400 g ball with an initial speed of 25 m/s. The initial velocity vector makes an angle of 40° with the horizontal. The wind blowing in the stadium applies a constant horizontal drag force of magnitude FD to the moving ball. As a result, the ball's displacement is divided by 2 compared to the ball's displacement if there is no drag force. Calculate FD.
A box of food is dropped from a humanitarian airplane. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the box when its speed reaches 30% of its terminal speed.
A man is riding a bicycle in a field. Seeing an obstacle, the man hits the brakes. As a result, the wheels get locked, and the bicycle slides a distance of 15 m on the ground before it stops. Given the coefficient of kinetic friction between the material of the bicycle tires and the ground to be 0.50, calculate the initial speed of the bicycle. Assume the ground is perfectly level.
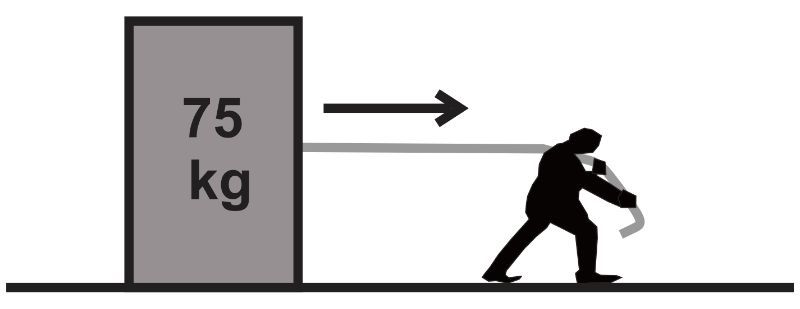
An industrial worker needs to move a 75-kg crate across a concrete floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the concrete floor is μₖ = 0.31. The worker applies a pulling force of 255N at an angle of 6.0° from the horizontal to slide the crate. Considering the setup, explain why the crate experiences a different acceleration when the force is applied at an angle compared to when the force is applied horizontally.