A closely wound rectangular coil of 80 turns has dimen-sions of 25.0 cm by 40.0 cm. The plane of the coil is rotated from a position where it makes an angle of 37.0° with a magnetic field of 1.70 T to a position perpendicular to the field. The rotation takes 0.0600 s. What is the average emf induced in the coil?
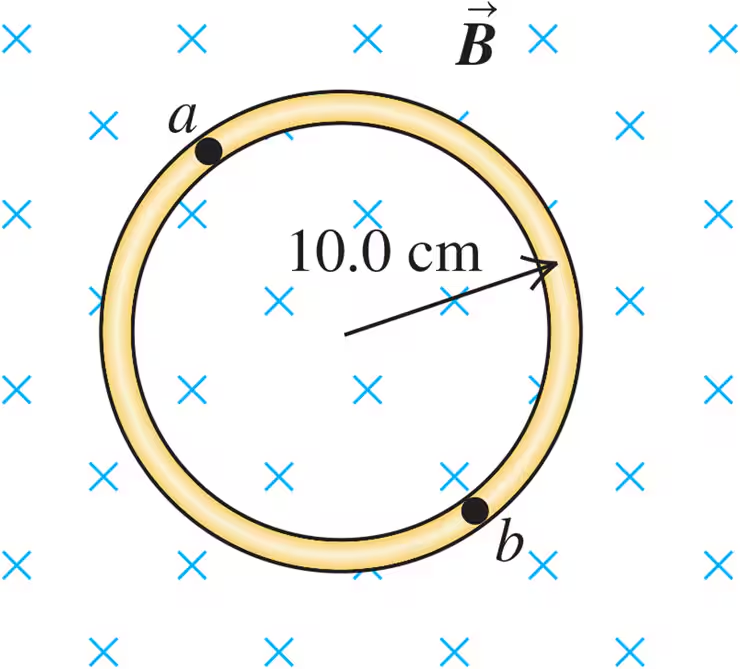
A circular loop of wire is in a region of spatially uniform magnetic field, as shown in Fig. E29.15. The magnetic field is directed into the plane of the figure. Determine the direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) of the induced current in the loop when (a) B is increasing; (b) B is decreasing; (c) B is constant with value B0. Explain your reasoning.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction

Lenz's Law

Magnetic Flux
The armature of a small generator consists of a flat, square coil with 120 turns and sides with a length of 1.60 cm. The coil rotates in a magnetic field of 0.0750 T. What is the angular speed of the coil if the maximum emf produced is 24.0 mV?
A flat, rectangular coil of dimensions l and w is pulled with uniform speed v through a uniform magnetic field B with the plane of its area perpendicular to the field (Fig. E29.14). (a) Find the emf induced in this coil. (b) If the speed and magnetic field are both tripled, what is the induced emf?
The current in Fig. obeys the equation , where . Find the direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) of the current induced in the round coil for .
Using Lenz's law, determine the direction of the current in resistor ab of Fig. E29.19 when (a) switch S is opened after having been closed for several minutes; (b) coil B is brought closer to coil A with the switch closed; (c) the resistance of R is decreased while the switch remains closed.
A cardboard tube is wrapped with two windings of insulated wire wound in opposite directions, as shown in Fig. E29.20. Terminals a and b of winding A may be connected to a battery through a reversing switch. State whether the induced current in the resistor R is from left to right or from right to left in the following circumstances: (a) the current in winding Ais from a to b and is increasing; (b) the current in winding A is from b to a and is decreasing; (c) the current in winding A is from b to a and is increasing.
