Which of the following determines the direction of gas movement?
a. Solubility in water
b. Partial pressure gradient
c. Temperature
d. Molecular weight and size of the gas molecule
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
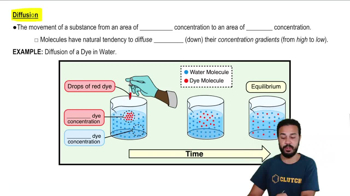

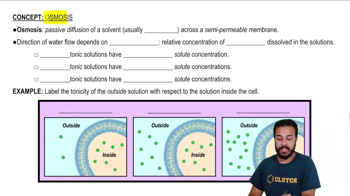
Which of the following determines the direction of gas movement?
a. Solubility in water
b. Partial pressure gradient
c. Temperature
d. Molecular weight and size of the gas molecule
When the inspiratory muscles contract:
a. The size of the thoracic cavity increases in diameter
b. The size of the thoracic cavity increases in length
c. The volume of the thoracic cavity decreases
d. The size of the thoracic cavity increases in both length and diameter
The nutrient blood supply of the lungs is provided by:
a. The pulmonary arteries
b. The aorta
c. The pulmonary veins
d. The bronchial arteries
Most oxygen carried in the blood is:
a. In solution in the plasma
b. Combined with plasma proteins
c. Chemically combined with the heme in red blood cells
d. In solution in the red blood cells
Which of the following has the greatest stimulating effect on the respiratory centers in the brain?
a. Oxygen
b. Carbon dioxide
c. Calcium
d. Willpower
In mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration, the rescuer blows air from his or her own respiratory system into that of the victim. Which of the following statements are correct?
(1) Expansion of the victim's lungs is brought about by blowing air in at higher than atmospheric pressure (positive-pressure breathing).
(2) During inflation of the lungs, the intrapleural pressure increases.
(3) This technique will not work if the victim has a hole in the chest wall, even if the lungs are intact.
(4) Expiration during this procedure depends on the elasticity of the alveolar and thoracic walls.
a. All of these
b. 1, 2, 4
c. 1, 2, 3
d. 1, 4