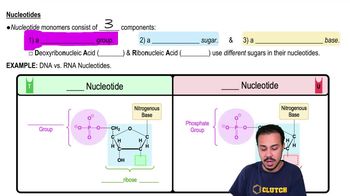
Textbook Question
Check your understanding of the flow of genetic information through a cell by filling in the blanks.
<IMAGE>
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
2096
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Check your understanding of the flow of genetic information through a cell by filling in the blanks.
<IMAGE>
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
What is the name of the process that produces RNA from a DNA template?
What is the name of the process that produces a polypeptide from an RNA template?
Scientists have discovered how to put together a bacteriophage with the protein coat of phage T2 and the DNA of phage lambda. If this composite phage were allowed to infect a bacterium, the phages produced in the host cell would have _________. (Explain your answer.)
a. The protein of T2 and the DNA of lambda
b. The protein of lambda and the DNA of T2
c. The protein and DNA of T2
d. The protein and DNA of lambda