Textbook Question
The diagram below shows the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus of a fluorine and a potassium atom. What kind of bond do you think would form between these two atoms?
2905
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
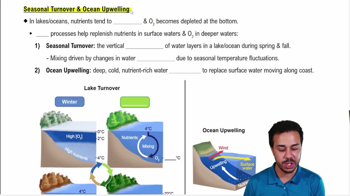


The diagram below shows the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus of a fluorine and a potassium atom. What kind of bond do you think would form between these two atoms?
This chapter explains how the emergent properties of water contribute to the suitability of the environment for life. Until fairly recently, scientists assumed that other physical requirements for life included a moderate range of temperature, pH, and atmospheric pressure. That view has changed with the discovery of organisms known as extremophiles, which have been found flourishing in hot, acidic sulfur springs and around hydrothermal vents deep in the ocean.
What does the existence of life in such environments say about the possibility of life on other planets?