
Anesthetics block pain by blocking the transmission of nerve signals. Which of these three chemicals might work as anesthetics? (Choose all that apply and explain your selections.)
a. A chemical that prevents the opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels in membranes
b. A chemical that inhibits the enzymes that degrade neurotransmitters
c. A chemical that blocks neurotransmitter receptors
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels
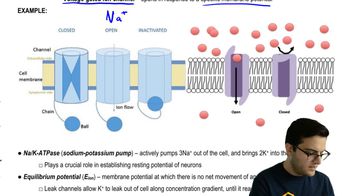
Neurotransmitter Degradation

Neurotransmitter Receptors

Joe accidentally touched a hot pan. His arm jerked back, and an instant later, he felt a burning pain. How would you explain the fact that his arm moved before he felt the pain?
a. His limbic system blocked the pain momentarily, but the important pain signals eventually got through.
b. His response was a spinal cord reflex that occurred before the pain signals reached the brain.
c. Motor neurons are myelinated; sensory neurons are not. The signals traveled faster to his muscles.
d. This scenario is not actually possible. The brain must register pain before a person can react.
Which division of the autonomic nervous system would you expect to be activated if a person heard an intruder at the front door?
a. Parasympathetic
b. Sympathetic
c. Enteric
A proposal to test an SSRI in a large number of individuals with depression was submitted to the FDA. Through random assignments, half of the patients would be controls, receiving nothing at all, and half the patients would receive the drug in pill form. Patients in both groups would note changes in their own mood in a daily journal. What flaw(s) do you note in this experimental design?
