
The inside of the neuron has a lower concentration of positive ions than the outside of the neuron. Is the membrane potential positive or negative?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Membrane Potential
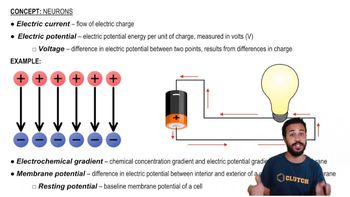
Ion Concentration Gradient

Resting Membrane Potential

Fill in the blanks to match some brain structures with their associated functions.
a. If the ___________ is severed, the right and left cerebral hemispheres cannot communicate.
b. The ___________ system helps store emotional memories.
c. Accounting for most of the weight of your brain is the highly folded ___________ ; it is the outer region of the ___________ .
d. The ___________ is responsible for hand-eye coordination.
e. The ___________ contains a cluster of neurons that function as the biological clock.
Joe accidentally touched a hot pan. His arm jerked back, and an instant later, he felt a burning pain. How would you explain the fact that his arm moved before he felt the pain?
a. His limbic system blocked the pain momentarily, but the important pain signals eventually got through.
b. His response was a spinal cord reflex that occurred before the pain signals reached the brain.
c. Motor neurons are myelinated; sensory neurons are not. The signals traveled faster to his muscles.
d. This scenario is not actually possible. The brain must register pain before a person can react.
