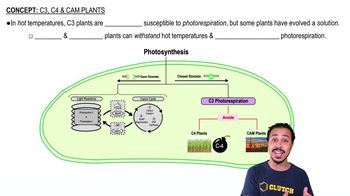
The reactions of the Calvin cycle are not directly dependent on light, but they usually do not occur at night. Why? (Explain your answer.)
a. It is often too cold at night for these reactions to take place.
b. Carbon dioxide concentrations decrease at night.
c. The Calvin cycle depends on products of the light reactions.
d. Plants usually close their stomata at night.