The mRNA formed from the repeating tetranucleotide UUAC incorporates only three amino acids, but the use of UAUC incorporates four amino acids. Why?

In the triplet binding technique, radioactivity remains on the filter when the amino acid corresponding to the codon is labeled. Explain the rationale for this technique.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
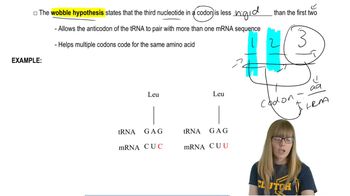
Triplet Binding Technique

Role of Radioactive Labeling
Codon-Anticodon Specificity
In studies using repeating copolymers, AC . . . incorporates threonine and histidine, and CAACAA . . . incorporates glutamine, asparagine, and threonine. What triplet code can definitely be assigned to threonine?
In a coding experiment using repeating copolymers, the following data were obtained:
AGG is known to code for arginine. Taking into account the wobble hypothesis, assign each of the four codons produced in the experiment to its correct amino acid.
When the amino acid sequences of insulin isolated from different organisms were determined, differences were noted. For example, alanine was substituted for threonine, serine for glycine, and valine for isoleucine at corresponding positions in the protein. List the single-base changes that could occur in codons of the genetic code to produce these amino acid changes.
In studies of the amino acid sequence of wild-type and mutant forms of tryptophan synthetase in E. coli, the following changes have been observed:
Determine a set of triplet codes in which only a single-nucleotide change produces each amino acid change.
Why doesn't polynucleotide phosphorylase (Ochoa's enzyme) synthesize RNA in vivo?

