Textbook Question
What experimental evidence provided the initial insights into the compositions of codons encoding specific amino acids?
632
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
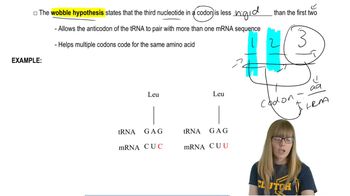
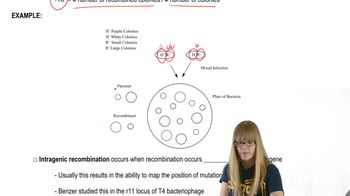

What experimental evidence provided the initial insights into the compositions of codons encoding specific amino acids?
How were the specific sequences of triplet codes determined experimentally?
Write a short essay that summarizes the key properties of the genetic code and the process by which RNA is transcribed on a DNA template.