Flower color may be red, white, or pink, and flower shape may be personate or peloric. For the following crosses, determine the P₁ and F₁ genotypes:

Given the inheritance pattern of coat color in rats described in Problem 17, predict the genotype and phenotype of the parents who produced the following offspring:
9/16 gray: 3/16 yellow: 3/16 black: 1/16 cream
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
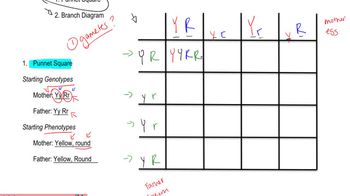
Mendelian Inheritance and Dihybrid Crosses
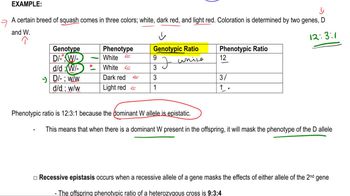
Epistasis and Coat Color Genetics
Genotype to Phenotype Prediction

In rats, the following genotypes of two independently assorting autosomal genes determine coat color:
A third gene pair on a separate autosome determines whether or not any color will be produced. The CC and Cc genotypes allow color according to the expression of the A and B alleles. However, the cc genotype results in albino rats regardless of the A and B alleles present. Determine the F₁ phenotypic ratio of the following crosses:
AAbbCC×aaBBcc
In rats, the following genotypes of two independently assorting autosomal genes determine coat color:
A third gene pair on a separate autosome determines whether or not any color will be produced. The CC and Cc genotypes allow color according to the expression of the A and B alleles. However, the cc genotype results in albino rats regardless of the A and B alleles present. Determine the F₁ phenotypic ratio of the following crosses:
AaBbCc×AaBbcc
Given the inheritance pattern of coat color in rats described in Problem 17, predict the genotype and phenotype of the parents who produced the following offspring:
9/16 gray: 3/16 yellow: 4/16 albino
Given the inheritance pattern of coat color in rats described in Problem 17, predict the genotype and phenotype of the parents who produced the following offspring: 27/64 gray:
16/64 albino: 9/64 yellow: 9/64 black: 3/64 cream
A husband and wife have normal vision, although both of their fathers are red–green color-blind, an inherited X-linked recessive condition. What is the probability that their first child will be (a) a normal son, (b) a normal daughter, (c) a color-blind son, (d) a color-blind daughter?
