The following segment of DNA is the template strand transcribed into mRNA:
5'-...GACATGGAA...-3'
What is the sequence of mRNA created from this sequence?

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 1 - The Molecular Basis of Heredity, Variation, and Evolution
Ch. 1 - The Molecular Basis of Heredity, Variation, and Evolution Problem 22a
Problem 22a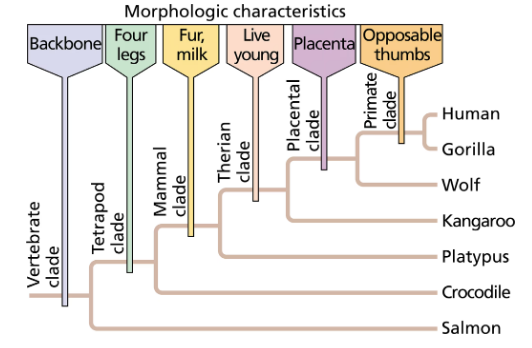
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



The following segment of DNA is the template strand transcribed into mRNA:
5'-...GACATGGAA...-3'
What is the sequence of mRNA created from this sequence?
The following segment of DNA is the template strand transcribed into mRNA:
5'-...GACATGGAA...-3'
What is the amino acid sequence produced by translation?
Using the following amino acid sequences obtained from different species of apes, construct a phylogenetic tree of the apes.
Examine the following figure and answer the following questions.
What characteristic is shared by all clades in the figure?
Examine the following figure and answer the following questions.
What characteristics are shared by the mammalian clade and the primate clade? What characteristic distinguishes the primates from other members of the mammalian clade?
Fill in the missing nucleotides (so there are three per block) and the missing amino acid abbreviations in the graphic shown here.