Textbook Question
For each of the following, note whether the component can be found in a virus, a cell, or both.
c. capsid
559
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

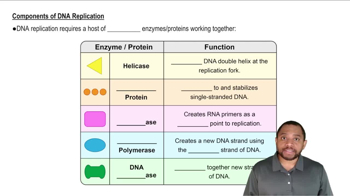
For each of the following, note whether the component can be found in a virus, a cell, or both.
c. capsid
For each of the following, note whether the component can be found in a virus, a cell, or both.
a. RNA
For each of the following, note whether the component can be found in a virus, a cell, or both.
c. ribosome
How does a vaccine protect against a viral disease?
Describe the function of a vector.
Describe the structure of a plasmid.