Textbook Question
Give the correct name for each of the following substituents:
(c) I―
1481
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Give the correct name for each of the following substituents:
(c) I―
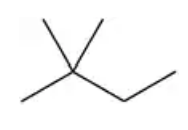
Draw the skeletal structure for each of the following compounds:
(a) 2,3-dimethylpentane
Draw the skeletal structure for each of the following compounds:
(a) 3-ethylhexane
Give the correct IUPAC name for each of the following compounds:
(c)
Give the correct IUPAC name for each of the following compounds:
(b)
What is the difference between a conformational isomer of a compound and a structural isomer of the same compound?