Glycogen and amylopectin are both branched polymers of glucose. Read the descriptions of each in Section 6.6. Which molecule has a more compact structure? Explain.

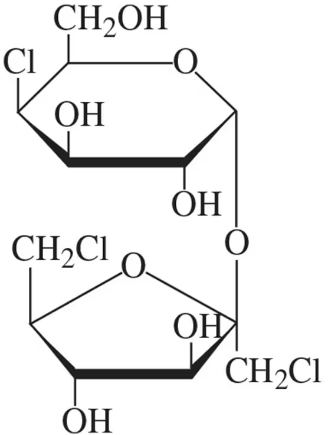
The structure of sucralose, found in the artificial sweetener Splenda, is shown in the figure. It consists of a chlorinated disaccharide made up of galactose and fructose. In its structure shown,
(a) identify the galactose unit and the fructose unit.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Disaccharides

Galactose

Fructose
On an exam, a student was asked to draw the Fischer projection of L-glucose, but he had only memorized the structure of D-glucose. He wrote the structure of D-glucose and switched the hydroxyl group on C5 from the right to the left. Was his answer correct? If not, what is the name of the aldose that he drew?
Carbohydrates are abbreviated using a three-letter abbreviation followed by their glycosidic bond type. For example, maltose and sucrose can be written respectively as
Provide the structure for the O-type blood carbohydrate set given the following abbreviation:
L-Fucα (1→2) Galß(1→4)GlcNAc
The structure of sucralose, found in the artificial sweetener Splenda, is shown in the figure. It consists of a chlorinated disaccharide made up of galactose and fructose. In its structure shown, (b) identify the type of glycosidic bond present.
Which of the components in starch is more likely to be broken down more quickly in plants, amylose or amylopectin? Why?
How much energy is produced if a person eats 50 g of digestible carbohydrate (not fiber) in a day? In this case, what percent of a 2200 Calorie diet would be digestible carbohydrate? Recall that carbohydrates provide four Calories of energy per gram consumed.
