Name the glycosidic bond present in mannobiose, shown in the following figure:
Ch.6 Carbohydrates Life's Sweet Molecules

Frost4th EditionGeneral, Organic and Biological ChemistryISBN: 9780134988696Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 3, Problem 39a
Identify a disaccharide that fits each of the following descriptions:
(a) ordinary table sugar
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the term 'disaccharide': A disaccharide is a carbohydrate composed of two monosaccharide units joined by a glycosidic bond. Common examples include sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Recall the common name for ordinary table sugar: Ordinary table sugar is chemically known as sucrose, which is a disaccharide.
Identify the monosaccharides that make up sucrose: Sucrose is composed of one glucose molecule and one fructose molecule linked by a glycosidic bond.
Recognize the source of sucrose: Sucrose is commonly derived from sugarcane or sugar beets and is widely used as a sweetener in food and beverages.
Confirm the description matches sucrose: Ordinary table sugar fits the description of a disaccharide commonly used in households and food preparation, confirming that sucrose is the correct answer.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are carbohydrates formed by the combination of two monosaccharides through a glycosidic bond. They are a type of simple sugar and can be broken down into their constituent monosaccharides by hydrolysis. Common examples include sucrose, lactose, and maltose, each serving different functions in biological systems.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Types of Disaccharides Concept 1
Sucrose
Sucrose is a specific disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose. It is commonly known as table sugar and is widely used as a sweetener in food and beverages. Sucrose is naturally found in many plants, particularly in sugarcane and sugar beets, and is a primary source of energy in the human diet.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Enzyme-Substrate Complex Example 1
Glycosidic Bond
A glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that links a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which can be another carbohydrate or a different type of molecule. In disaccharides, this bond forms between the hydroxyl group of one sugar and the anomeric carbon of another, resulting in the release of a water molecule during the reaction. This bond is crucial for the formation and stability of disaccharides.
Recommended video:
Guided course
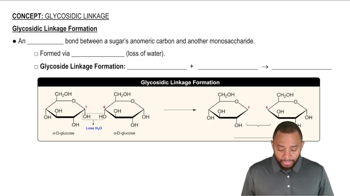
Glycosidic Linkage Formation Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
746
views
Textbook Question
For each of the following disaccharides, name the glycosidic bond and draw the monosaccharide units produced by hydrolysis:
(a)
831
views
Textbook Question
Lactulose is a disaccharide used in the treatment of chronic constipation. Its formal name is galactose β(1→4) fructose.
(a) Draw the structure of lactulose.
696
views
Textbook Question
Based on the sweetness index in Table 6.2, if you tasted a drop of each of the syrups below, which would taste the sweetest?
(a) light corn syrup (100% glucose)
640
views
Textbook Question
If one sweetener packet of Splenda, Sweet’N Low, or Equal has the same sweetness as two tablespoons of sugar, according to Table 6.2, which of the packets contains the smallest amount of the sweetener?
642
views
Textbook Question
Describe the similarities and differences of the following polysaccharides:
(a) amylose and amylopectin
590
views
