Name and describe the three states of matter.

Which of these terms, (i) mixture, (ii) solid, (iii) liquid, (iv) gas, (v) chemical element, (vi) chemical compound, applies to the following substances at room temperature?
a. Gasoline
b. Iodine
c. Water
d. Air
e. Blood
f. Sodium bicarbonate
g. Gaseous ammonia
h. Silicon
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
States of Matter

Mixtures vs. Pure Substances

Chemical Elements and Compounds
Name two changes of state and describe what causes each to occur.
Butane (C4H8) is an easily compressible gas used in cigarette lighters. It has a melting point of and a boiling point of -138.4 °C and a boiling point of -0.5 °C. Would you expect a butane lighter to work in winter when the temperature outdoors is 25 °F? Why or why not?
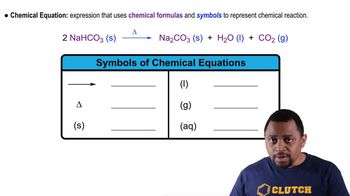
Hydrogen peroxide, often used in solutions to cleanse cuts and scrapes, breaks down to yield water and oxygen: Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2(aq) → Hydrogen, H2(g) + Oxygen, O2(g)
b. Which of the substances are chemical compounds, and which are elements?
Glucose, a form of sugar, has the formula C6H12O6. Which elements are included in this compound, and how many atoms of each are present?
Write the formula for ibuprofen: 13 carbons, 18 hydrogens, and 2 oxygens. What are the common uses of ibuprofen?
