Use your answer from Problem 7.54 to calculate the following:
a. [O2] at equilibrium when [CO2] = 0.18 mol/L and [CO] = 0.0200 mol/L

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Use your answer from Problem 7.54 to calculate the following:
a. [O2] at equilibrium when [CO2] = 0.18 mol/L and [CO] = 0.0200 mol/L
Oxygen can be converted into ozone by the action of lightning or electric sparks:
3 O2(g) ⇌ 2 O3(g)
For this reaction, ∆H = +69kcal/mol (+285 kj/mol) and K = 2.68 × 10-29 at 25 °C.
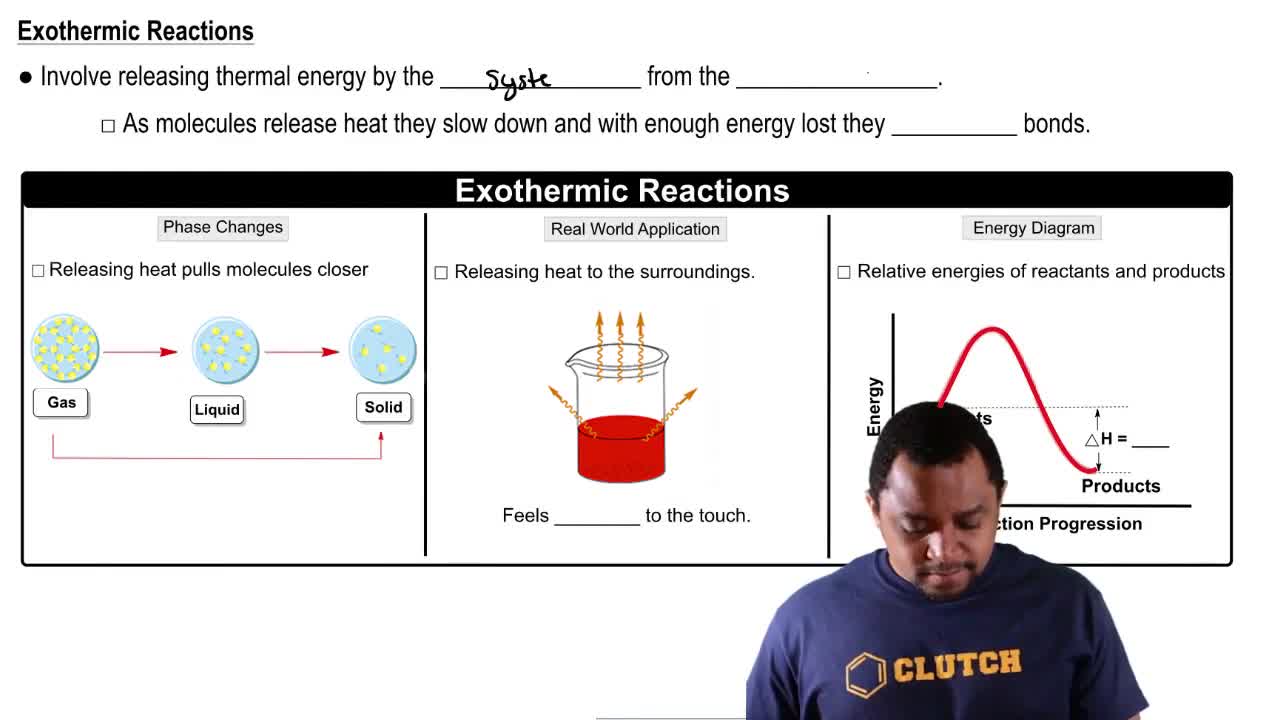
a. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Oxygen can be converted into ozone by the action of lightning or electric sparks:
3 O2(g) ⇌ 2 O3(g)
For this reaction, ∆H = +69kcal/mol (+285 kj/mol) and K = 2.68 × 10-29 at 25 °C.
b. Are the reactants or the products favored at equilibrium?
When the following equilibria are disturbed by increasing the pressure, does the concentration of reaction products increase, decrease, or remain the same?
a. 2 CO2(g) ⇌ 2 CO(g) + O2(g)
For the following equilibria, use Le Châtelier's principle to predict the direction of the reaction when the pressure is increased by decreasing the volume of the equilibrium mixture.
a. C(s) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO(g) + H2(g)
The reaction CO(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO2(g) + H2(g) has ∆H = -9.8 kcal/mol (-41 kJ/mol). Does the amount of H2 in an equilibrium mixture increase or decrease when the temperature is decreased?