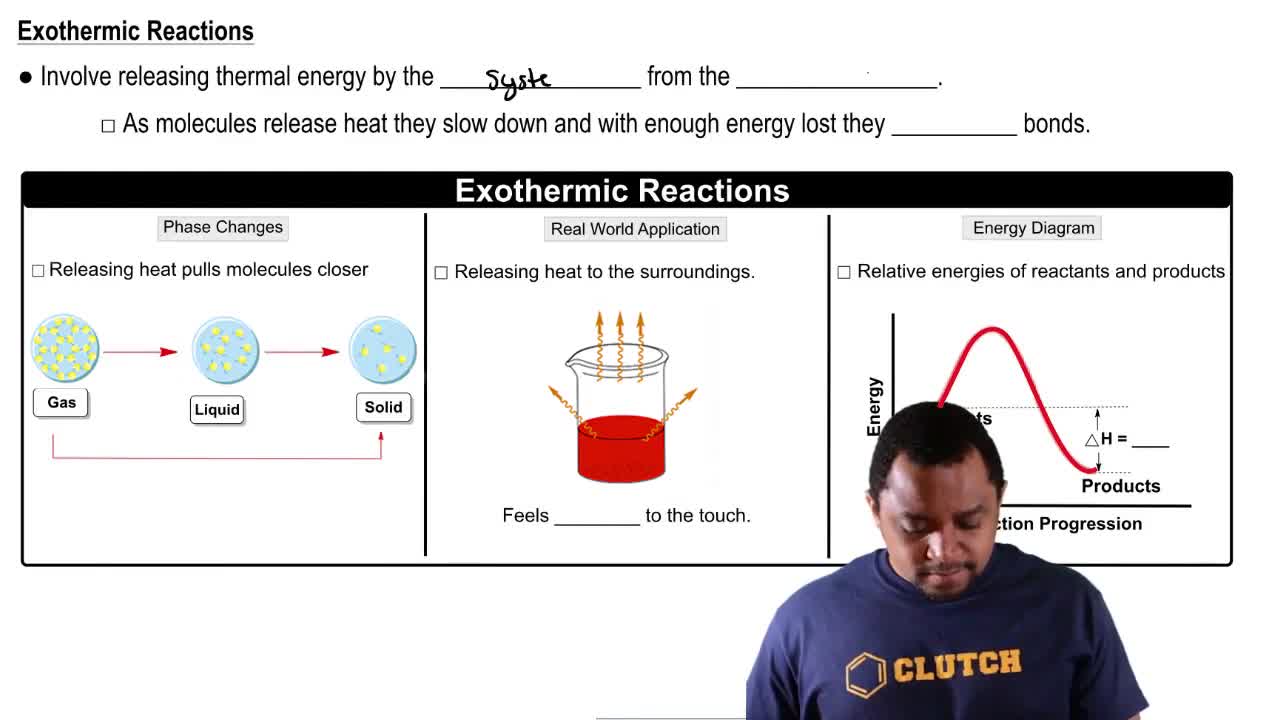
Hydrogen chloride can be made from the reaction of chlorine and hydrogen:
Cl2(g) + H2(g) → 2 HCl(g)
For this reaction, K = 26 × 1033 and ∆H = -44 kcal/mol(-184 kJ/mol) at 25 °C.
a. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Hydrogen chloride can be made from the reaction of chlorine and hydrogen:
Cl2(g) + H2(g) → 2 HCl(g)
For this reaction, K = 26 × 1033 and ∆H = -44 kcal/mol(-184 kJ/mol) at 25 °C.
a. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?
When the following equilibria are disturbed by increasing the pressure, does the concentration of reaction products increase, decrease, or remain the same?
a. 2 CO2(g) ⇌ 2 CO(g) + O2(g)
For the following equilibria, use Le Châtelier's principle to predict the direction of the reaction when the pressure is increased by decreasing the volume of the equilibrium mixture.
a. C(s) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO(g) + H2(g)
The reaction H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2 HI(g) has ∆H = -2.2 kcal/mol (-9.2 kJ/mol). Will the equilibrium concentration of HI increase or decrease when
b. H2 is removed?
The reaction H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2 HI(g) has ∆H = -2.2 kcal/mol (-9.2 kJ/mol). Will the equilibrium concentration of HI increase or decrease when
c. A catalyst is added?
The reaction Fe3+(aq) + Cl-(aq) ⇌ FeCl2+(aq) is endothermic. How will the equilibrium concentration of FeCl2+ change when
b. Cl- is precipitated by addition of AgNO3?