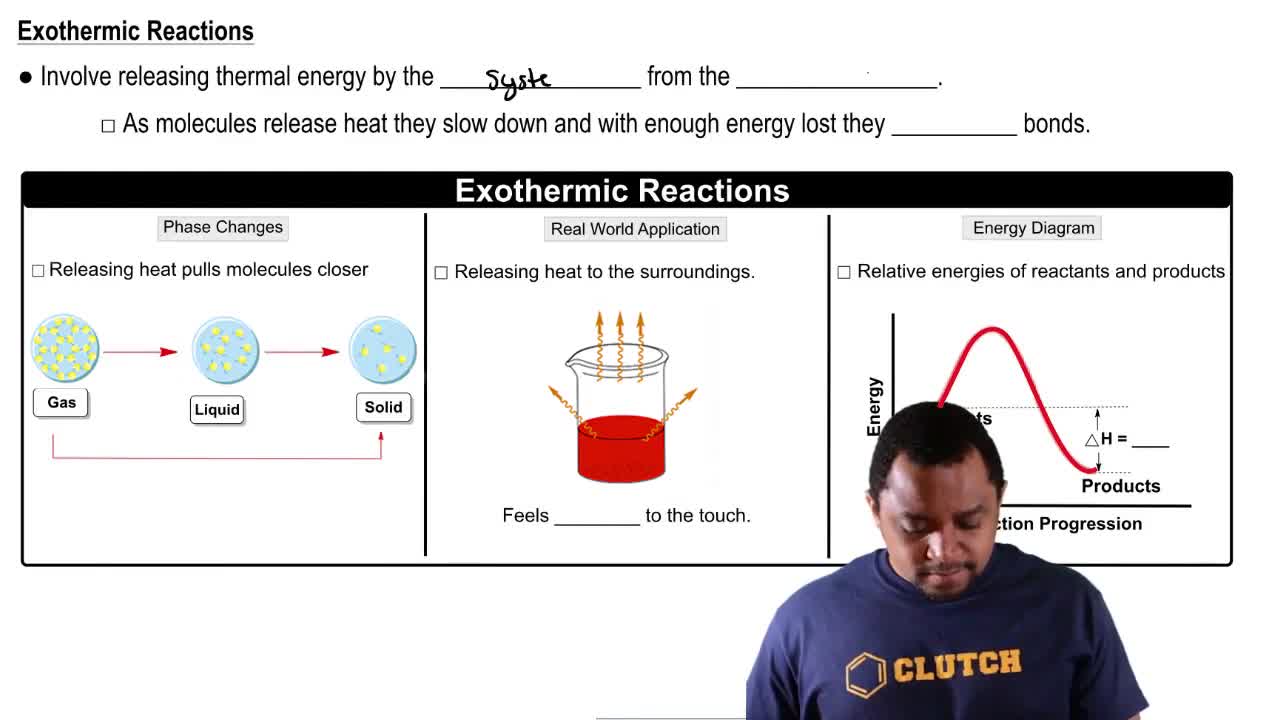
Based on bond energies, which atmospheric gas in each pair do you think is more stable? Explain.
a. O2 or N2
b. CO or CO2

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Based on bond energies, which atmospheric gas in each pair do you think is more stable? Explain.
a. O2 or N2
b. CO or CO2
In photosynthesis, green plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (C6H12O6) according to the following equation:
6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) → C6H12O6(aq) + 6 O2(g)
a. Estimate ∆H for the reaction using bond dissociation energies from Table 7.1. Give your answer in kcal/mol and kJ/mol. (C6H12O6 has five C―C bonds, seven C―H bonds, seven C―O bonds, and five O―H bonds).
The following equation shows the conversion of aluminum oxide (from the ore bauxite) to aluminum:
2 Al2O3(s) → 4 Al(s) + 3 O2(g) ∆H = +801 kcal/mol (+3350 kJ/mol)
c. How many kilocalories are required to produce 10.0 g of aluminum? How many kilojoules?
Does entropy increase or decrease in the following processes?
a. Polymeric complex carbohydrates are metabolized by the body, converted into smaller simple sugars.
Does entropy increase or decrease in the following processes?
c. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g)