Textbook Question
For the reaction
b. Does entropy increase or decrease in this process?
1614
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
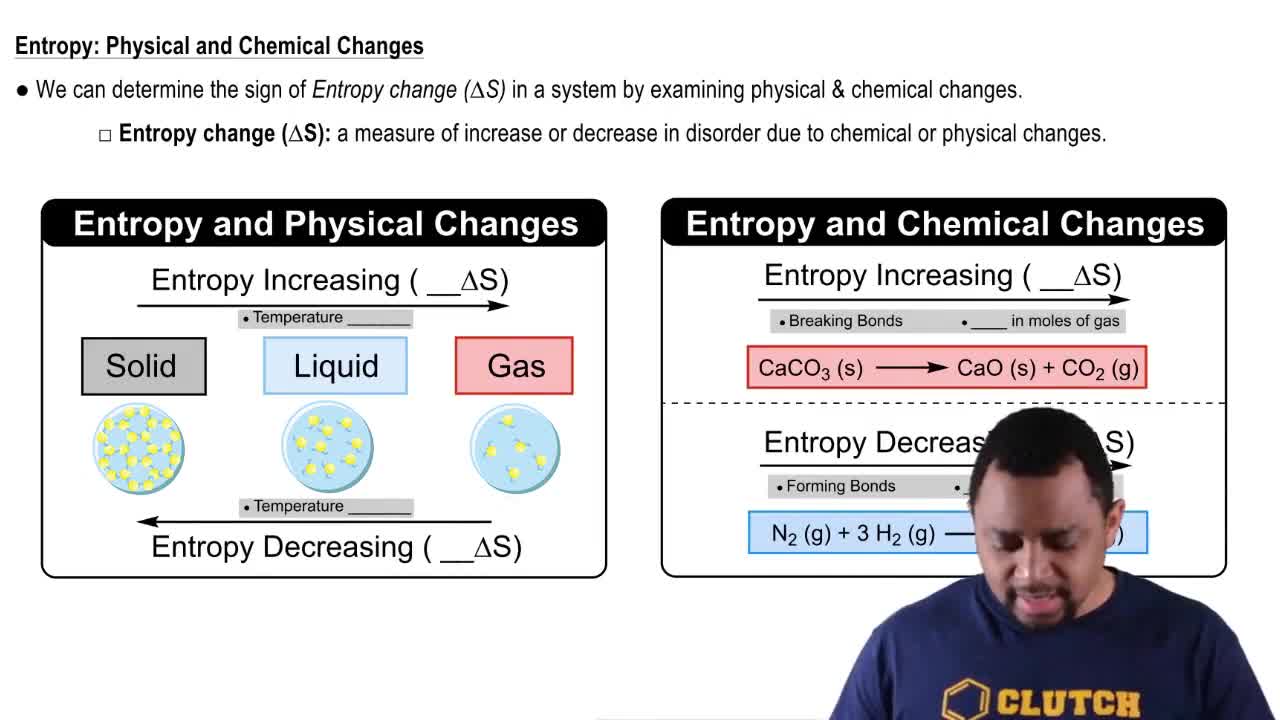

For the reaction
b. Does entropy increase or decrease in this process?
For the reaction 2 Hg(l) + O2(g) → 2 HgO(s), ∆H = –43 kcal/mol (–180 kJ/mol).
a. Does entropy increase or decrease in this process? Explain.
For the reaction 2 Hg(l) + O2(g) → 2 HgO(s), ∆H = –43 kcal/mol (–180 kJ/mol).
b. Under what conditions would you expect this process to be spontaneous?
Which reaction is faster, one with Eact = +10 kcal/mol(+41.8 kJ/mol) or one with Eact = +5 kcal/mol(+20.9 kJ/mol)? Explain.
Why does increasing concentration generally increase the rate of a reaction?
What is a catalyst, and what effect does it have on the activation energy of a reaction?