The text discusses three forms of enzyme inhibition: uncompetitive inhibition, competitive inhibition, and irreversible inhibition.
b. What kinds of bonds are formed between an enzyme and each of these three kinds of inhibitors?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

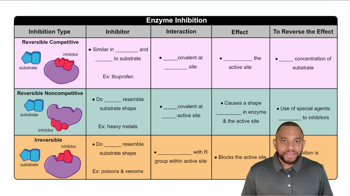
The text discusses three forms of enzyme inhibition: uncompetitive inhibition, competitive inhibition, and irreversible inhibition.
b. What kinds of bonds are formed between an enzyme and each of these three kinds of inhibitors?
What kind of inhibition (uncompetitive, competitive, or irreversible) is present in each of the following:
a. Penicillin is used to treat certain bacterial infections. Penicillin is effective because it binds to the enzyme glycopeptide transpeptidase and does not dissociate.
What kind of inhibition (uncompetitive, competitive, or irreversible) is present in each of the following:
c. The antibiotic deoxycycline inhibits the bacterial enzyme collagenase, slowing bacterial growth. Deoxycycline does not fit into the active site of collagenase and binds elsewhere on the enzyme.
The meat tenderizer used in cooking is primarily papain, a protease enzyme isolated from the fruit of the papaya tree. Why do you suppose papain is so effective at tenderizing meat?
Why do allosteric enzymes have two types of binding sites?
What are the cellular advantages to feedback inhibition?