Textbook Question
Identify each step in glycolysis that is an isomerization.
1525
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

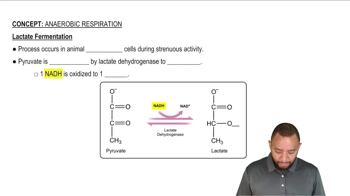

Identify each step in glycolysis that is an isomerization.
In Figure 22.3, compare the starting compound (glucose) and the final product (pyruvate).
a. Which is oxidized to a greater extent?
Use curved arrows (like those in Figure 22.3) to write an equation for the conversion of fructose to fructose 6-phosphate by ATP. At what step does fructose 6-phosphate enter glycolysis?