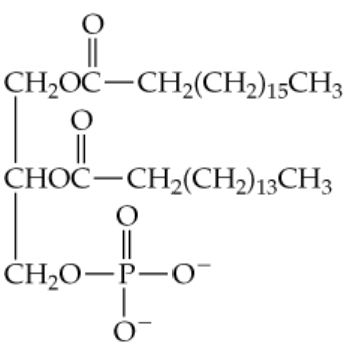
Textbook Question
One of the constituents of the carnauba wax used in floor and furniture polish is an ester of a 32-carbon straight-chain alcohol with a C20:0 straight-chain carboxylic acid. Draw the structure of this ester. (Use subscripts to show the numbers of connected CH2 groups.)
984
views