Textbook Question
Use Figure 23.1 to identify the family of lipids to which each of these molecules belongs.
b.
888
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
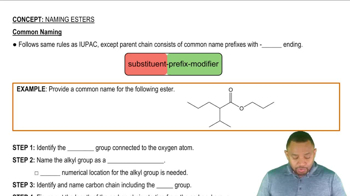


Use Figure 23.1 to identify the family of lipids to which each of these molecules belongs.
b.
Draw the complete structural formula of arachidonic acid (Table 23.1) in a way that shows the cis stereochemistry of its four double bonds.
Can there be any chiral carbon atoms in triacylglycerols? If so, which ones can be chiral and what determines their chirality?
Write an equation for the complete hydrogenation of triolein, the triacylglycerol with three oleic acid acyl groups for which you drew the structure in Problem 23.3. Name the fatty acid from which the resulting acyl groups are derived.