Textbook Question
What is a mole?
2665
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

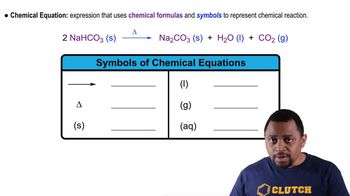

What is a mole?
What is Avogadro's number?
Calculate the molar mass for each of the following:
b. C3H6O3
Calculate the molar mass for each of the following:
a. Al2(SO4)3, antiperspirant
Calculate the mass, in grams, for each of the following:
d. 0.145 mole of C2H6O
Calculate the mass, in grams, for each of the following:
e. 2.08 moles of (NH4)2SO4