You can search and get more information about test score reports here.
How to interpret your scores
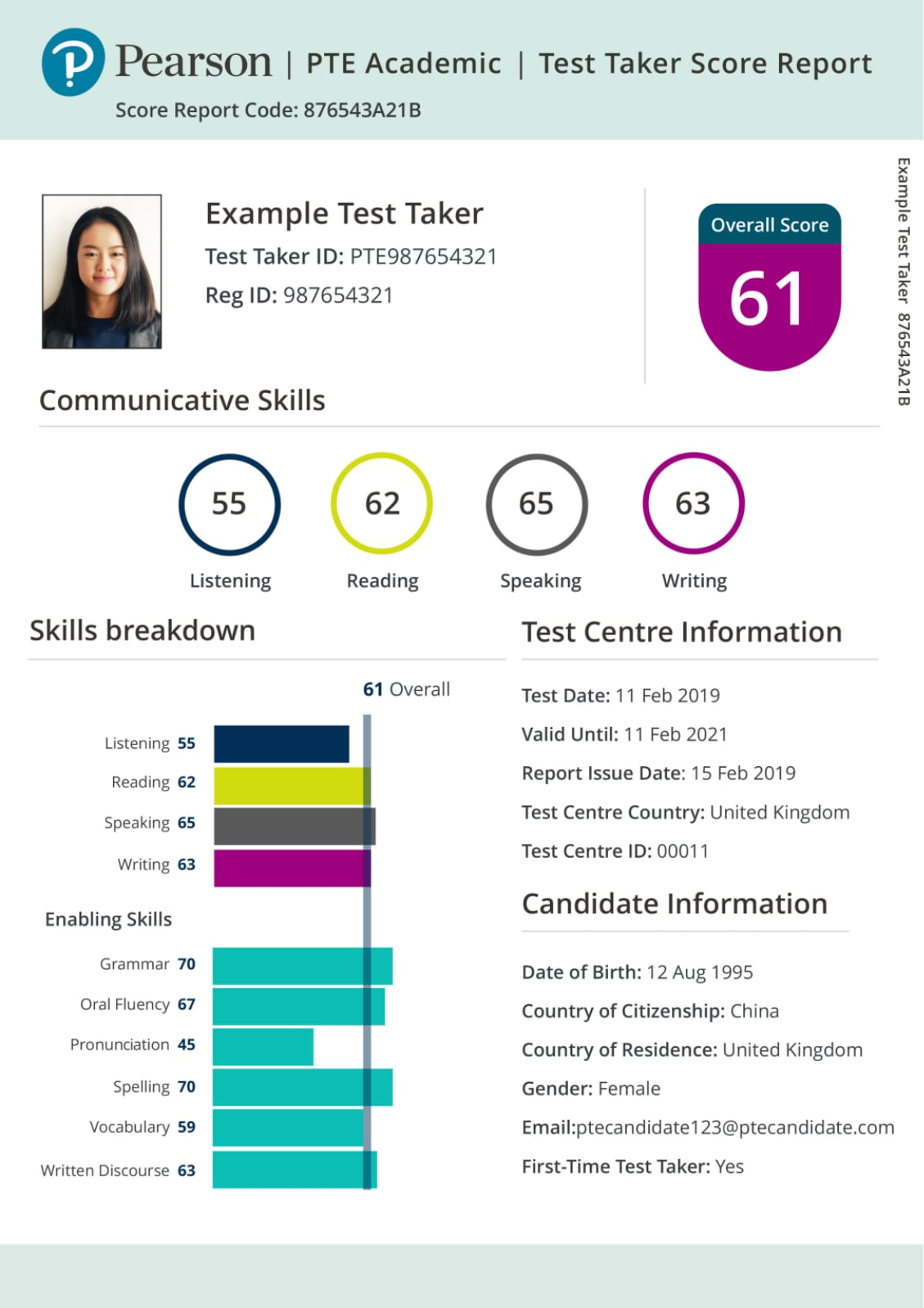
It's essential to recognize that every element of the test is scored, including correct pronunciation and oral fluency in speaking tasks, grammar and vocabulary in writing, as well as comprehension and summarizing skills in reading and listening sections.
A closer look at this sample score report reveals more details about the skill breakdown, grammar, oral fluency and vocabulary, which are also vital components considered by universities to judge your command of English.
Applying scores to university entry requirements
When it comes to university entry requirements, institutions have varying benchmarks for PTE scores. Typically, universities require an overall score and may also have specific band requirements for each module.
For example, a university might require an overall PTE score of 65 with no band score less than 50 in each test module.
What score do I need to get into university?
No entry requirement is the same, and it depends on the course and university. It's important to look up what the universities you like need. You can find this on their website or by asking their admissions office.
Postgraduate courses generally require a higher score than undergraduate ones. Courses that require the student to have a deeper understanding of the English language to comprehend the subject will also generally require a high score level.
What is a good PTE score?
There isn't a good or bad score. Your language learning score reflects your efforts and skills, and shows areas needing improvement. The score's significance lies in what it means for your learning journey and goals.
My test score is lower than the required amount
It's important to talk to the universities you've applied for. Sometimes they can be more flexible with their entry requirements than they show on their websites. By talking directly to the admissions teams, you can understand how your PTE scores fit in.
If your scores are a bit low, they might look at other parts of your application to see your skills. So, don't be afraid to ask questions and find out how to improve your application. If you aren’t completely confident you're going to reach your test goal. You can also take our scored practice tests to see if and where you need to improve your English skills.
Some universities may offer conditional acceptance, allowing students to enroll in English language preparatory courses or exams if their PTE scores fall slightly short. Make sure to check with them to see if they have extra courses you can take.
Which universities accept PTE?
The PTE Academic test is globally recognized and accepted by numerous countries for university admissions, making it a valuable asset for international students.
Predominantly, countries such as the UK, Australia, New Zealand, Canada and the United States offer a wide range of universities and colleges that acknowledge the PTE test scores as proof of English language proficiency. In the UK and Australia, for instance, the PTE test is widely accepted across all higher education institutions, including some of the world's top universities.
Meanwhile, in Canada and the USA, an increasing number of institutions are starting to recognize the value of PTE scores.
PTE scores are accepted not only in English-speaking countries but also in non-English speaking countries with English programs. Prospective students should check individual university requirements before applying, as they may differ by country and institution. You can find the full list here.
A gateway to opportunity
Your PTE test scores open doors to global education. Understand the scoring system for universities to ease your application. Use scores to assess your level, improve language skills and clarify university needs for your goals to come true.
Every test taker is unique, so customize your preparation to your needs and strengths. With dedication, confidence and practice, you can achieve PTE success and confidently find your place in the academic world.
Find out and learn more on the PTE website and see where your English skills can take you. Good luck!