Textbook Question
List the order of nucleotides on the mRNA that would be transcribed from the following DNA sequence: CGATTACTTA.
2404
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

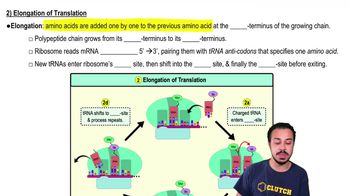

Transcription ________.
a. Synthesizes new daughter DNA molecules from an existing DNA molecule
b. Results in the synthesis of an RNA copy of a gene
c. Pairs thymines (T) with adenines (A)
d. Occurs on ribosomes
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
a. Carries monosaccharides to the ribosome for synthesis
b. Is made of messenger RNA
c. Has an anticodon region that is complementary to the mRNA codon
d. Is the site of protein synthesis
During the process of transcription, ________.
a. DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of more DNA.
b. DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of RNA.
c. DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of proteins.
d. RNA serves as a template for the synthesis of proteins.