Textbook Question
To ensure adequate nitrogen for a crop, a farmer would want to decrease _________ by soil bacteria.
a. Nitrification
b. Denitrification
c. Nitrogen fixation
d. a and c
845
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


To ensure adequate nitrogen for a crop, a farmer would want to decrease _________ by soil bacteria.
a. Nitrification
b. Denitrification
c. Nitrogen fixation
d. a and c
Which of the following best illustrates ecological succession?
a. A mouse eats seeds, and an owl eats the mouse.
b. Decomposition in soil releases nitrogen that plants can use.
c. Grasses grow in a deserted field, followed by shrubs and then trees.
d. Imported pheasants increase in numbers, while local quail disappear.
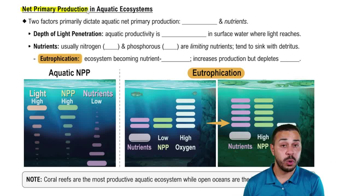
What is rapid eutrophication? What steps might be taken to slow this process?