
A geneticist found that a particular mutation had no effect on the polypeptide encoded by a gene. This mutation probably involved
a. Deletion of one nucleotide
b. Alteration of the start codon
c. Insertion of one nucleotide
d. Substitution of one nucleotide
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Silent Mutation
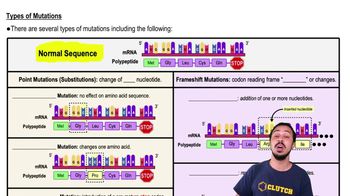
Types of Mutations

Codon and Amino Acid Relationship

What is the name of the process that produces RNA from a DNA template?
What is the name of the process that produces a polypeptide from an RNA template?
Scientists have discovered how to put together a bacteriophage with the protein coat of phage T2 and the DNA of phage lambda. If this composite phage were allowed to infect a bacterium, the phages produced in the host cell would have _________. (Explain your answer.)
a. The protein of T2 and the DNA of lambda
b. The protein of lambda and the DNA of T2
c. The protein and DNA of T2
d. The protein and DNA of lambda
The nucleotide sequence of a DNA codon is GTA. A messenger RNA molecule with a complementary codon is transcribed from the DNA. In the process of protein synthesis, a transfer RNA pairs with the mRNA codon. What is the nucleotide sequence of the tRNA anticodon?
a. CAT
b. CUT
c. GUA
d. CAU
