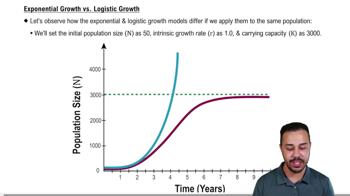
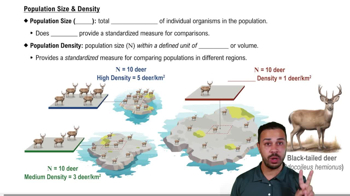
After seeds have sprouted, gardeners often pull up some of the seedlings so that only a few grow to maturity. How does this practice help produce the best yield?
a. By increasing K
b. By decreasing r
c. By reducing intraspecific competition
d. By adding a density-independent factor to the environment