Which of the following is one of the major components of the plasma membrane of a plant cell?
a. Phospholipids
b. Cellulose fibers
c. Collagen fibers
d. Pectins

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


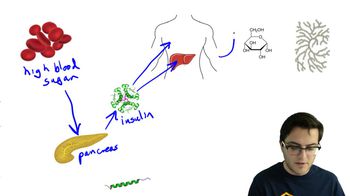
Which of the following is one of the major components of the plasma membrane of a plant cell?
a. Phospholipids
b. Cellulose fibers
c. Collagen fibers
d. Pectins
In which cell would you find the most smooth ER?
a. Pancreatic cell that secretes digestive enzymes
b. Ovarian cell that produces estrogen (a steroid hormone)
c. Muscle cell in the thigh of a long-distance runner
d. White blood cell that engulfs bacteria
In which cell would you find the most rough ER?
a. Pancreatic cell that secretes digestive enzymes
b. Ovarian cell that produces estrogen (a steroid hormone)
c. Muscle cell in the thigh of a long-distance runner
d. White blood cell that engulfs bacteria
In which cell would you find the most mitochondria?
a. Pancreatic cell that secretes digestive enzymes
b. Ovarian cell that produces estrogen (a steroid hormone)
c. Muscle cell in the thigh of a long-distance runner
d. White blood cell that engulfs bacteria