Label the structures in this diagram of an animal cell. Review the functions of each of these organelles.
<IMAGE>

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
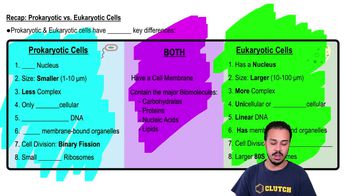


Label the structures in this diagram of an animal cell. Review the functions of each of these organelles.
<IMAGE>
The ultrastructure of a chloroplast is best studied using a
a. Light microscope
b. Scanning electron microscope
c. Transmission electron microscope
d. Light microscope and fluorescent dyes
The cells of an ant and an elephant are, on average, the same small size; an elephant just has more of them. What is the main advantage of small cell size? (Explain your reasoning.)
a. A small cell has a larger plasma membrane surface area than does a large cell.
b. Small cells can better take up sufficient nutrients and oxygen to service their cell volume.
c. It takes less energy to make an organism out of small cells.
d. Small cells require less oxygen than do large cells.
Which of the following is one of the major components of the plasma membrane of a plant cell?
a. Phospholipids
b. Cellulose fibers
c. Collagen fibers
d. Pectins