Back
BackProblem 1
In the primate phylogenetic tree below, fill in groups (a)–(e). Of the groups, which are anthropoids and which are apes?

Problem 2
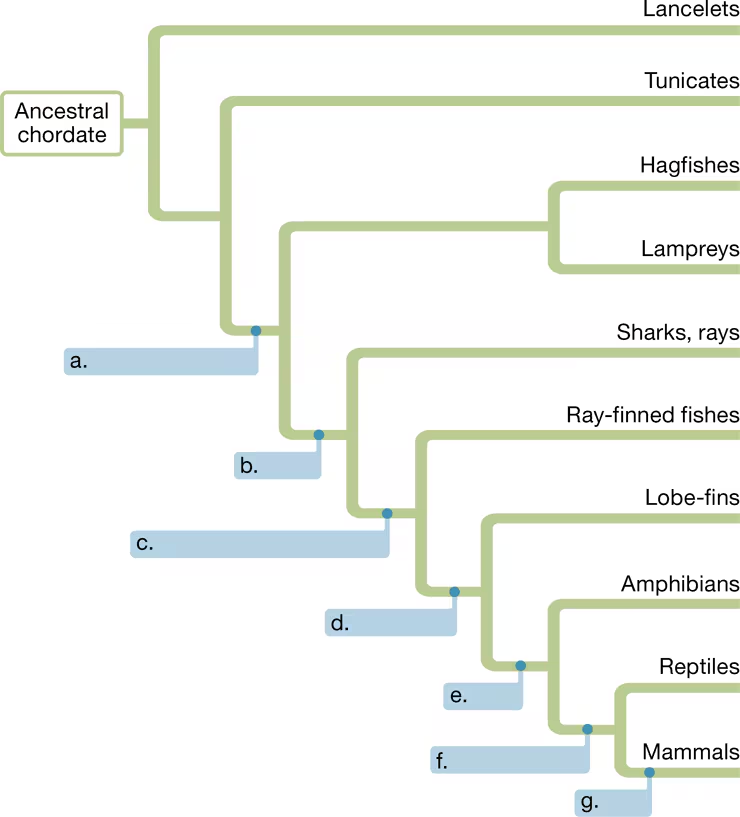
In the chordate phylogenetic tree below, fill in the shared derived character that defines each clade.
Problem 3
A lamprey, a shark, a lizard, and a rabbit share all the following characteristics except
a. Pharyngeal slits in the embryo or adult.
b. Vertebrae.
c. Hinged jaws.
d. A dorsal, hollow nerve cord.
Problem 4
Why were the Tiktaalik fossils an exciting discovery for scientists studying tetrapod evolution?
a. They are the earliest frog-like animal discovered to date.
b. They show that tetrapods successfully colonized land much earlier than previously thought.
c. They have a roughly equal combination of fishlike and tetrapod-like characteristics.
d. They demonstrate conclusively that limbs evolved as lobe-fins dragged themselves from pond to pond during droughts.
Problem 5
Fossils suggest that the first major trait distinguishing hominins from other primates was
a. A larger brain.
b. Erect posture.
c. Forward-facing eyes with depth perception.
d. Tool making.
Problem 6
Which of the following correctly lists possible ancestors of humans from the oldest to the most recent?
a. Homo erectus, Australopithecus, Homo habilis
b. Australopithecus, Homo habilis, Homo erectus
c. Australopithecus, Homo erectus, Homo habilis
d. Homo ergaster, Homo erectus, Homo neanderthalensis
Problem 7
Which of these is not a member of the anthropoids?
a. Chimpanzee
b. Tarsier
c. Human
d. New World monkey
Problem 8
Studies of DNA support which of the following?
a. Members of the group called australopiths were the first to migrate from Africa.
b. Homo sapiens originated in Africa.
c. Sahelanthropus was the earliest hominin.
d. Chimpanzees are more similar to gorillas and orangutans than to humans.
Problem 9
The earliest members of the genus Homo
a. Had a larger brain compared to other hominins.
b. Probably hunted dinosaurs.
c. Lived about 4 million years ago.
d. Were the first hominins to be bipedal.
- Compare the adaptations of amphibians and reptiles for terrestrial life.
Problem 10
- Birds and mammals are both endothermic, and both have four-chambered hearts. Most reptiles are ectothermic and have three-chambered hearts. Why don't biologists group birds with mammals? Why do most biologists now consider birds to be reptiles?
Problem 11
Problem 12
One of the misconceptions about human evolution is expressed in the question 'If chimpanzees were our ancestors, then why do chimpanzees still exist?' Use Figure 19.10A to explain the answer.
- What adaptations inherited from our primate ancestors enable humans to make and use tools?
Problem 13
- Summarize the hypotheses that explain variation in human skin color as adaptations to variation in UV radiation.
Problem 14
Problem 15
A good scientific hypothesis is based on existing evidence and leads to testable predictions. What hypothesis did the paleontologists who discovered Tiktaalik test? What evidence did they use to predict where they would find fossils of transitional forms?
- Explain some of the reasons why the human species has been able to expand in number and distribution to a greater extent than most other animals.
Problem 16
- Anthropologists are interested in locating areas in Africa where fossils 4–8 million years old might be found. Why?
Problem 17
Problem 18
By measuring the fossil remains of Homo floresiensis, scientists have estimated its weight to be around 32.5 kg and its brain volume to be roughly 420 cm3. Plot these values on the graph in Figure 19.13A. Which hominin has the most similar relationship of brain volume to body mass? Does this information support the hypothesis that H. floresiensis is a dwarf form of H. erectus, or an alternative hypothesis? Explain.