
Cells lining kidney tubules function in the reabsorption of water from urine. In response to chemical signals, they reversibly insert additional aquaporins into their plasma membranes. In which of these situations would your tubule cells have the most aquaporins: after a long run on a hot day, right after a large meal, or after drinking a large bottle of water? Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Aquaporins
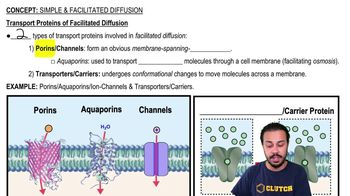
Kidney Function and Water Reabsorption
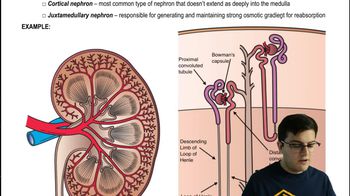
Physiological Responses to Hydration Status

How do the components and structure of cell membranes relate to the functions of membranes?
Mercury is known to inhibit the permeability of water channels. To help establish that the protein isolated by Agre's group was a water channel, the researchers incubated groups of RNA-injected oocytes (which thus made aquaporin proteins) in four different solutions: plain buffer, low concentration and high concentration of a mercury chloride (HgCl₂) solution, and low concentration of a mercury solution followed by an agent (ME) known to reverse the effects of mercury. The water permeability of the cells was determined by the rate of their osmotic swelling. Interpret the results of this experiment, which are presented in the graph below. Control oocytes not injected with aquaporin RNA were also incubated with buffer and the two concentrations of mercury. Predict what the results of these treatments would be.
<IMAGE>
A biologist performed two series of experiments on lactase, the enzyme that hydrolyzes lactose to glucose and galactose. First, she made up 10% lactose solutions containing different concentrations of enzyme and measured the rate at which galactose was produced (grams of galactose per minute). Results of these experiments are shown in Table A below. In the second series of experiments (Table B), she prepared 2% enzyme solutions containing different concentrations of lactose and again measured the rate of galactose production.
Graph and explain the relationship between the reaction rate and the enzyme concentration.
<IMAGE>
A biologist performed two series of experiments on lactase, the enzyme that hydrolyzes lactose to glucose and galactose. First, she made up 10% lactose solutions containing different concentrations of enzyme and measured the rate at which galactose was produced (grams of galactose per minute). Results of these experiments are shown in Table A below. In the second series of experiments (Table B), she prepared 2% enzyme solutions containing different concentrations of lactose and again measured the rate of galactose production.
Graph and explain the relationship between the reaction rate and the substrate concentration. How and why did the results of the two experiments differ?.
<IMAGE>
