Textbook Question
Predict whether a precipitation reaction will occur when aqueous solutions of the following substances are mixed. For those that form a precipitate, write the net ionic reaction. (b)
301
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


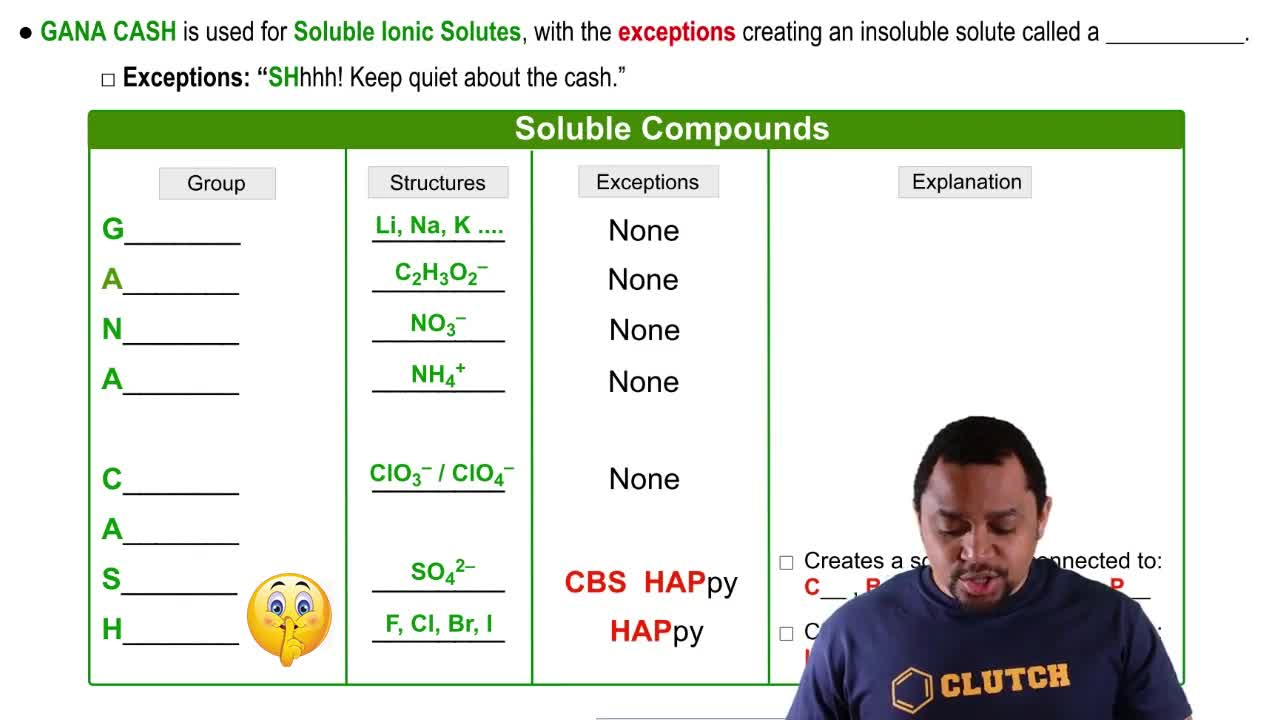
Predict whether a precipitation reaction will occur when aqueous solutions of the following substances are mixed. For those that form a precipitate, write the net ionic reaction. (b)
Predict whether a precipitation reaction will occur when aqueous solutions of the following substances are mixed. For those that form a precipitate, write the net ionic reaction. (c)
Predict whether a precipitation reaction will occur when aqueous solutions of the following substances are mixed. For those that form a precipitate, write the net ionic reaction. (d)
How would you prepare the following substances by a precipitation reaction? (a) PbSO4
How would you prepare the following substances by a precipitation reaction? (b) Mg3(PO4)2