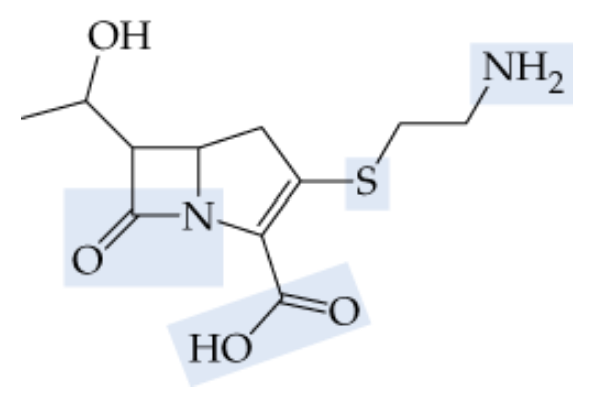
Textbook Question
Draw the structural formulas and name all cyclic isomers with the formula C5H10.
866
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Draw the structural formulas and name all cyclic isomers with the formula C5H10.
Propane, commonly known as liquid petroleum (LP) gas, burns in air to yield CO2 and H2O. Write a balanced equation for the reaction.
Write the formulas of the three doubly brominated isomers formed when 2-methylpropane reacts with Br2 in the presence of light.
The line structure for pregabalin (Lyrica) is shown as follows:
Identify carbons a–d as primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary.
Which do you think has a higher boiling point, pentane or neopentane (2,2-dimethylpropane)? Why?