Textbook Question
The following names are incorrect. Tell what is wrong with each, and provide the correct names.
c.
990
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
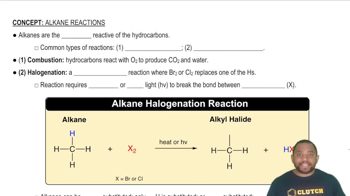


The following names are incorrect. Tell what is wrong with each, and provide the correct names.
c.
The following names are incorrect. Write the structural formula that agrees with the apparent name, and then write the correct name of the compound
a. 2-Ethylbutane
Draw the structural formulas and name all cyclic isomers with the formula C5H10.
Write the formulas of the three doubly brominated isomers formed when 2-methylpropane reacts with Br2 in the presence of light.
Identify the indicated functional groups in the following molecules:
b. Thienamycin, an antibiotic
The line structure for pregabalin (Lyrica) is shown as follows:
Identify carbons a–d as primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary.