Textbook Question
Consider the following tripeptide:
b. Give the one-letter and three-letter abbreviations of this tripeptide.
396
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
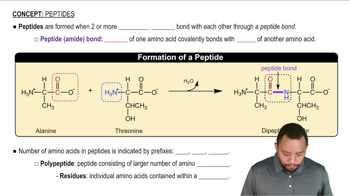

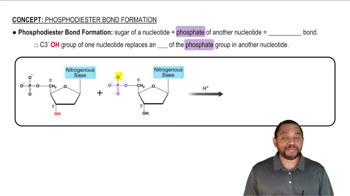
Consider the following tripeptide:
b. Give the one-letter and three-letter abbreviations of this tripeptide.
Draw the structural formula for each of the following peptides:
b. KCG
Draw the structural formula for each of the following peptides:
c. His—Met—Gln
Draw the structural formula for each of the following peptides:
d. IYP
Identify the N-terminus and the C-terminus for each of the peptides in Problem 10.18.
a. Ala—Asn—Thr
b. DS
Identify the N-terminus and the C-terminus for each of the peptides in Problem 10.18.
c. Val—Arg