Textbook Question
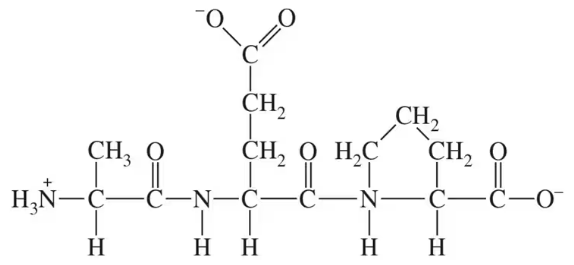
Write the products for the following condensation or hydrolysis reactions:
a.
553
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Write the products for the following condensation or hydrolysis reactions:
a.
Write the products for the following condensation or hydrolysis reactions:
a.
Consider the following tripeptide:
a. Circle the N-terminal amino acid, and give its name. Draw a square around the C-terminal amino acid, and give its name.
Draw the structural formula for each of the following peptides:
b. KCG
Draw the structural formula for each of the following peptides:
c. His—Met—Gln
Draw the structural formula for each of the following peptides:
c. Val—Arg